Hello everyone, I am Om Ashish Soni, Software Engineer at Mastercard, Top Competitive Coder from India, 3x Gold Medalist, 2x Published AI researcher, Gate Topper & Computer Engineer.
We will go step by step journey for competitive programming and Data Structures and Algorithms
- MNCs and Medium size companies takes coding round & technical rounds in interview there they ask for data structures and algorithms problems.
- Lot of real world problems can be solved very easily by using dsa.
- This boosts your critical thinking, cognitive thinking, debugging and implementation skills, which helps infinitely as a future Software Engineer.
CP vs DSA :
- DSA is helpful for placement, Competitive Coding is super set of DSA.
- Competitive Coding is more like a game, brain sport, where people compete using human brain to solve any problem. DSA is more or less structured way of preparing for tech interviews.
- Competitive Coding changes the fundamental way of thinking and tackling real world problems of life.
Personal Opinion :
- If I was in my 1st / 2nd / 3rd year of college, I would start CP & DSA from today itself.
- It’s never late to start.
- C++ , Java, Python ( pypy3 )
- Learn the basics of language from youtube, geeksforgeeks, w3schools Learn about data types, operators, function, syntax, etc.
Start solving picked language problems on hackerrank ( Any 1 language ):
- Once you do any one of the above, you will have some grip on problem solving and language specific.
- If you are not able to solve any problem, don’t giveup try the compile time and run time errors solution looking on google, stack overflow, geeks for geeks etc.
- Atleast try for 10–20 times before looking at solution.
Start your problem solving with pattern printing problems
- You by do pattern printing in any language, that helps building logic.
- Pattern Printing Tutorial by Striver
Practice :
Before we jump on learning various data structures and algorithms these are few general resources you may refer for any topic.
- Striver youtube
- Take U Forward Youtube
- Apna College C++ Placement Course ( for basic to advanced )
- LUV Youtube Channel [ good for c++ ]
- My Code School
- Tushar Roy ( for algorithms )
- Tech dose ( for data structures and algorithms)
- Vivek Gupta ( for competitive programming and some advanced topics )
below is super helpful blog containing topic list
- Best blog for dsa and competitive coding topics & guide GeeksForGeeks
- CP Algorithms
- Codeforces Blogs
- Om Ashish Soni Competitive Programming Github Repo
- Whatever data structures , algorithms you learn implement them and store in your own github repo
- Start learning array, string in your chosen language from youtube, geeksforgeeks, etc.
- Practice them on Hackerrank.
- If you feel comfortable then start solving array and string easy problems on leetcode.com / geeksforgeeks.org
Practice :
Before you do some more practice it is important to know what is best way and best practices to solve and practice problems.
- LeetCode Problemset
- CSES Problemset
- Codeforces Problemset
- Striver SDE Sheet Problemset [ Highly Recommended for Interviews ]
- Geeksforgeeks Problems [ Alternative for LeetCode Premium ]
- Striver A2Z Sheet [ Recommended for interviews ]
- Filter problems like below highlighted from easy to medium to hard,
- Solve easy first gradually moving to medium, keep hard for some later time.
- Visit to leetcode.com, select a specific topic and start solving easy problems on it.
- The more number of accepted solutions means the more easy problem is.
Topic-Wise Practice:
- Focused practice on a specific topic ensures you master the underlying concepts and techniques.
- It helps build confidence and prepares you to handle problems of that particular type with ease.
Random Problem-Solving:
- Solving random problems simulates real competition scenarios where you don’t know the topic beforehand.
- It trains you to identify the relevant topic and approach for solving the problem.
- This practice improves adaptability, problem-recognition skills, and overall versatility as a programmer.
-
Have pen and paper,
-
Read problem twice
-
Read constraints twice
-
List all approaches you can think of
-
Dry run all tests cases with your hand on paper
-
Now whatever you did see how can you code for it
-
Atleast try for 1–2 hours before giving up
-
Still can’t get it, try to see the topics
-
Still can’t get it, try to see hint 1,2,…
-
Still can’t get it, try to read blogs of other people’s solution, read approach and code if needed
-
Still can’t get it, then watch video
-
After you solve with editorials then observe what you missed
- Math, Number Theory are all school level topics, for example primality, factorization, odd — even number, GCD, LCM etc.
- Bit manipulation may be something new, may need to learn. Each number in the machine will be represented at the end using 0s and 1s, these are the problems based on bits. Binary Operations like bitwise AND, OR, NOT, XOR etc.
Resources :
- Maths for CP & DSA by Utkarsh Gupta
- Maths by LUV
- Bit Manipulation by Striver
- Hackerearth Number Theory Blog
Practice Problems :
- Number Theory Problems Leetcode
- Mathematics problems on CSES sheet
- Practice problems on above topics on leetcode, gfg, codeforces
- Codechef and Hackerearth are specifically good for math and bit manip problems.
- In c++ there is important concept called as bitset<>
- Time Complexity ( TC ) & Space Complexity ( SC ) are not the topics, but they are important in order to understand
- Time complexity gives an idea of execution time independent of language.
- Space complexity gives an idea of space used execution of program independent of language.
- Learn master’s theorem to prove / find time complexity.
- Learn what is recursion stack and how it uses space in recursive programs.
Resources :
- Time Complexity Tutorial by LUV
- Time Complexity by Striver
- Time and Space Complexity Blog on GeeksForGeeks
- Try to dig for time and space complexity for the problems you solve.
- Selection Sort
- Bubble Sort [ optional — nice to learn]
- Insertion Sort
- Merge Sort ( Requires Recusion to implement )
- Quick Sort
- Heap Sort ( optional — may keep this for later )
- In built sorting algorithms in languages i.e. cpp, java, python
Resources
Practice Problems
- Searching and Sorting CSES [ pick only sorting problems ]
- Sorting problems on Leetcode
Tips
- Don’t rush for learning all sorting algorithms, but try to understand them
- Try to use inbuilt sorting most of the time when you are solving problem.
- Note : Binary Search can only be applied on Sorted Array / Data Structures. [ function needs to be monotonic in order to apply Binary Search ]
Resources :
- Binary Search GeeksForGeeks
- Binary Search Basic to Advanced Boot Camp by Striver
- Binary Search By Take U Forward / Striver
- Binary Search by Errichto
- Some other resources by default in any topic is apna college c++ playlist, luv, striver , take u forward on youtube.
- You may just search on youtube for a topic.
Other Variations on Binary Search :
Practice Problems :
- Searching and Sorting CSES [ pick only searching problems ]
- Solve problems on searching and sorting
Learn linkedlist, stack and queue
Linked List
- https://takeuforward.org/linked-list/linked-list-introduction
- Linkedlist Tutorial Apna College
- Leetcode Linkedlist Problems
Stack
Queue
- STL Library implementation of data structures C++
- All data structures are readily available like vectors ( array ) , stack, queue, list , linkedlist, priority queue in all languages.
- So learn and implment only for learning purpose
- while problem solving use ready made data strucutres
- For example libraries like C++ STL , Java Collections, and same for python.
- Search your topic name on google, i.e. stack on geeksforgeeks
- Read and understand the implementation code of stack from geeksforgeeks
- Try to implement it on your own without copying.
- Test your code by solving some problem related to this topic on leetcode / geeksfogeeks.
- Learn Standard Template Library in C++, or in java Collections, or similarly for python.
- C++ STL Tutorial, Java Collections Tutorial
- Learn about Vector, Map, Set.
- For running and writing programs you may use IDE like VS Code, Sublime Text, or any online ide like Jdoodle.
Greedy
- This is not an algorithm, it is strategy.
- Greedy is human way of thinking in order to reachout the solution.
- problem types includes, searching , sorting etc. any greedy strategy to reachout solution.
- Actually Sorting and Searching are at the end Greedy only.
- Greedy Tutorial Striver
- Leetcode Greedy Problems
Sliding Window
- This linear greedy problem solving technique by maintaining window over array ( linear data structure ) and solving optimization problems.
- Geeks for Geeks Sliding Window
- Leetcode Sliding Window Practice
- Two pointers & Sliding window Striver
Two Pointer
- Technique of maintaining 2 pointers ( left and right ) it is more general version of sliding window, and more powerful then sliding window.
- Apna College Two Pointer Tutorial
- Geeskforgeeks Two Pointer
- CSES Searching and Sorting Section
Recursion is calling function by itself, is the great stregth to solve difficult problems easily
Recursion by Sanket Singh Part -1, 2 and 3
Practice Problems :
learn divide and conquer technique in that recursion is heavily used there.
- Backtracking is bruteforce way to solve a problem using recursion, but backtracking limits recursion tree.
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/backtracking-algorithms/
- https://leetcode.com/problem-list/backtracking/
- Practice problems on leetcode and geeksforgeeks
Contest is competition of competitive programming
They hosts regularly contests on weekly/ biweekly/ monthly basis
- Calendar for contests : https://clist.by/ If you perform better your rating will increase and vice versa
- These platforms ratings matters sometimes in your interview, offcampus and oncampus shortlisting for placements.
- Contests gives you expirence on time pressure.
Recommended contests :
- Leecode weekly and biweekly ( for placement & competitive coding )
- Codeforces div 2,3,4 ( for competitive coder folks )
- Atcoder beginner Contests ( for beginners and intermediates )
- Geeksforgeeks weekend contest ( Just to keep momentum )
- Apart from above there are some other like Meta Hackercup.
So what you are waiting for just start competing.
- Hashing is a technique and a data structure which is used to store key value pair.
- HashMap<> in java, unordered_map in C++, dict in python, object in js.
- Hashing by Striver
- Apna College Hashing Tutorial 1, Hashing in C++ STL
- What is Hashing Geeks For Geeks
- Hashing all resources Geeks For Geeks
Practice Problems :
Usually Tree is extension of linkedlist / vector
- Tree data structure is a hierarchical structure that is used to represent and organize data in the form of parent child relationship.
- Geeks For Geeks Tree Blog
- Striver Tree Series
- All topics of Trees Geeks For Geeks
Trees : 1. Binary Tree
- Each node in tree has left &/ right children.
- tree traversal , preorder, inorder and postorder
- recursively solving tree problems
- concepts like what is subtree, leaf, root and all.
- Solve tree problems on leetcode and geeksforgeeks
Practice Problems :
2. Binary Search Tree
- Binary Search Tree is Binary Tree in the order of values of nodes.
- Inorder traversal gives you sorted values.
- Binary Search idea comes from here only.
Practice Problems :
CSES Tree Algorithms Problems
Tree Problems by Om Ashish Soni
Solve above topics on leetcode, geeksforgeeks, ( codeforces — for competitive coders )
There are also other type of trees like rooted ( n-ary ) , un-rooted ( n-ary ) tree.
Heap and Priority Queue ( Priority Queue is implemented using heap )
- Heap is a tree data structure along with the additional propery of ordering by value of nodes.
- max and min heap are major types of heap
- Heap tutorial by Apna College
- GeeksForGeeks heap data structure
- Priority Queue in C++ STL
Practice Problems :
Dijsoint Set Union ( DSU ) :
Pracitce Problems :
- Node, Edge, Cycle, Loop, Path, in graph.
- Directed, Undirected, Asyclic Graph,
- Memory representation ( data structure ) of graph
-
Adjacency Matrix
-
Adjacency List
- Bredth First Search ( BFS ) , Depth First Search ( DFS )
- DFS is most useful
- Single Source Shortest Path ( Dijsktra , Bellman Ford )
- All Shortest Path ( Floyd Warshall )
- Dijsktra is very usefull
- Minimum spanning tree in graph ( Prims, Kruskal Algorithm )
- Prims, kruskal, connected componenets of graph
- kosaraju algo, articulation points of graph ( tarjans algorithm )
- priority queue and dijsoint set union if you can learn will help more to solve these graph algo problems
Ooooppps ! the most obsessfull topic you may think
Actually its very easy to solve and implement if you know it and hands on it.
If you don’t remember the past, you are condemned to repeat it.
- Overlapping subproblems property
- We decompose the problem in smaller subproblems and then we solve sub problems and reusing already stored solution.
- DP problems are optimization problems like minimizing, maximizing,
- DP is also used with combinatorics which we will see later.
- DP can be combined with any topic, binary search, string, graph, tree any thing.
There are 2 types of DP :
- Tabulation ( Iterative — Tabular ) — Easy to solve and implement in longer time, more widely used
- Memoization ( Recursive ) — Good to start with
Great start for dp ( don’t focus on language of video , focus on topic )
takeuforward is the best place to learn data structures, algorithms, most asked coding interview questions, real…
takeuforward.org](https://takeuforward.org/dynamic-programming/striver-dp-series-dynamic-programming-problems?source=post_page-----09789df3df55--------------------------------)
- We already would have covered this in math section, but if it is pending
- You may start thinking to do combinatorics now
- Since sometimes combinatorics implementation requires dp.
- https://leetcode.com/problem-list/combinatorics/
- Leetcode, Codechef, Codeforces, GFG are good for combinatorics.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M5PbeUrOsDw
A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and…
- Whole list of topic above
- Keep learning other advanced techniques and ds
- like segment tree, fenwick tree, policy based data structures
- Keep giving contests
- Keep upsolving problems.
- See all topics here :
- https://github.com/om-ashish-soni/Competitive-Programming/tree/master/problemset/topic_wise_problems
- Pay Attention to Problem Statement: Take extra care to read the problem statement correctly. Mistakes in understanding the problem can lead to wrong solutions. For example, distinguishing between “undirectional” and “unidirectional” graphs (undirected vs directed) can significantly impact the approach.
- Analyze the Constraints: Understanding the problem constraints can provide valuable insights into choosing the appropriate algorithms and data structures to solve the problem effectively.
- Stuck in a Contest: If you feel stuck during a contest, take a short break of 1 or 2 minutes. Wash your face to refresh yourself and then start again with a clear mind.
- Can't Improve: If you're struggling to improve, try upsolving. If you can't come up with any ideas, refer to the editorial. If there is an unfamiliar topic, learn it and repeat this process.
- How to Boost Performance: Participating in long challenges on Codechef can help boost your performance and allow you to learn various tips and techniques.
- Combining Different Approaches to Solve Problems: When faced with a problem, try multiple approaches. For example, if it's a graph problem, start with DFS. If that's not enough, try using disjoint sets. If there's a need for path compression, use it. If the constraints allow, consider using Fenwick trees. This approach helps you combine different techniques to solve problems effectively.
- Difficulty with Last 3 to 4 Problems of a Contest: If your basics are clear, practice a lot of problems related to trees, graphs, dynamic programming, and segment trees until you feel satisfied.
- Where and How to Practice:
- Hackerrank is a good platform for beginners to learn a programming language.
- Once you have a basic grip on a language, move to the problem set on Codeforces.
- Solve problems on Codeforces with ratings below 1000.
- Practice problems based on specific topics from the Codeforces problem set.
- Participate in contests on Codeforces and Codechef.
- Upsolve problems. If you can't solve a problem within 30 minutes, refer to the editorial. Learn any unfamiliar topics and repeat this process.
- As your rating improves, continue step 4 and solve problems within the rating range of [your rating - 100, your rating + 100].
- Keep learning new algorithms and practice implementing them.
- How Problem Setters Find New Problems: Not all problems in contests are built from scratch. Many problems are a mixture of multiple problems from resources like the CSES Problem Set.
- Getting TLE with String as a Key in Ordered Map: If you're experiencing performance issues with a string as a key in an ordered map, try using a hash map instead. This change may improve the performance.
- IDE Recommendation: In competitive programming, it's recommended not to use an IDE. Instead, develop a habit of using a text editor like Vim, this is optional you may avoid it.
- Which Template Should I Use in CP?: There are various templates available for competitive programming. You can refer to the following resource for templates that are useful in competitive coding: Templates Useful for CP
- Tips to solve Constuctive :
- Writing a brute force script rather than manual solving
- Finding a pattern
- Coding optimized solution corresponding to pattern
- Taking care of edge cases.
Follow Om Ashish Soni, for more such content.
If you have any questions or would like to collaborate, reach out to me. I’m always excited to discuss new ideas and opportunities.
- Email: [email protected]
- LinkedIn: @om-ashish-soni LinkedIn
- Twitter: @om_ashish_soni Twitter
- YouTube: @om_ashish_soni YouTube
- Hugging Face : @om-ashish-soni HuggingFace
The codes provided in this repository are written based on my personal preferences. Although they are public, I continue to use this repository for participating in contests. Therefore, please ensure that you take appropriate measures to protect your code against plagiarism.
| Contests for Newcomers |
|---|
| Contest 1 |
| DSA and Interview Preparation |
|---|
| LeetCode |
| GeeksForGeeks |
| InterviewBit |
| CodingNinjas |
| Binary Search (currently down) |
| Useful resources for learning |
|---|
| Good Tutorials for Competitive Programming |
| EKZLib |
| Handy tools for contests |
|---|
| Graph Editor - CSAcademy |
| OEIS - The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences |
- AtCoder Standings
- Codeforces Contest List
- Virtual Judge
- Codeforces Profile Comparator
- USACO Contests Guide
- Codeforces Recommender by CodeDrills
- Codeforces - C++ Tricks
- Codeforces - Useful C++ Tricks
- Codeforces - C++ Optimization Techniques
- Codeforces - Cool C++ Features
- C++ Reference - cppreference.com
- LearnCpp.com - C++ Tutorial
-
Pay Attention to Problem Statement: Take extra care to read the problem statement correctly. Mistakes in understanding the problem can lead to wrong solutions. For example, distinguishing between "undirectional" and "unidirectional" graphs (undirected vs directed) can significantly impact the approach.
-
Analyze the Constraints: Understanding the problem constraints can provide valuable insights into choosing the appropriate algorithms and data structures to solve the problem effectively.
- Om Ashish Soni's Competitive Programming Repository
- KTH Competitive Programming Repository
- USACO Implementations by Benjamin Qi
- VisuAlgo - Visualizing Algorithms and Data Structures
- Topcoder Data Science Tutorials
- CS97SI - Introduction to Competitive Programming from Stanford University
- Codeforces Problemset
- AtCoder Contest Archive
- Saraswati Online Judge
- CodeChef
- HackerRank Dashboard
- CSAcademy Contest Archive
- TLX - Toki Learning Center
- Kattis Open
- USACO Guide - Practicing
- Codeforces - Guide to Problem Solving
- Informatics Notes - Preparing for Contests
- Programming and Problem Solving (PAPS) by USACO Guide
- Competitive Programming Handbook (CPH) by USACO Guide
- Competitive Programming in C++ by Darren Yao
- Practice on Codeforces: Solve a lot of problems on Codeforces that are just above your current rating range.
- Prioritize Codeforces: Codeforces is the best platform to improve your competitive programming skills, so spend a significant amount of time on it.
- AtCoder: Participate in AtCoder Beginner Contests, which are suitable for beginners and provide valuable practice. You can also try AtCoder Regular Contests.
- Codechef: Use Codechef for math and bit manipulation questions.
- Codechef Starters Contests: Participating in Codechef Starters Contests can be beneficial.
- LeetCode: Solve LeetCode Weekly and Biweekly Contests for practice and warm-up. These contests often have a mix of easy and medium difficulty questions, which can boost your motivation.
- Awesome Resources: Explore the following resources for inspiration and motivation:
-
Stuck in a Contest: If you feel stuck during a contest, take a short break of 1 or 2 minutes. Wash your face to refresh yourself and then start again with a clear mind.
-
Can't Improve: If you're struggling to improve, try upsolving. If you can't come up with any ideas, refer to the editorial. If there is an unfamiliar topic, learn it and repeat this process.
-
How to Boost Performance: Participating in long challenges on Codechef can help boost your performance and allow you to learn various tips and techniques.
-
Combining Different Approaches to Solve Problems: When faced with a problem, try multiple approaches. For example, if it's a graph problem, start with DFS. If that's not enough, try using disjoint sets. If there's a need for path compression, use it. If the constraints allow, consider using Fenwick trees. This approach helps you combine different techniques to solve problems effectively.
-
Difficulty with Last 3 to 4 Problems of a Contest: If your basics are clear, practice a lot of problems related to trees, graphs, dynamic programming, and segment trees until you feel satisfied.
-
Where and How to Practice:
- Hackerrank is a good platform for beginners to learn a programming language.
- Once you have a basic grip on a language, move to the problem set on Codeforces.
- Solve problems on Codeforces with ratings below 1000.
- Practice problems based on specific topics from the Codeforces problem set.
- Participate in contests on Codeforces and Codechef.
- Upsolve problems. If you can't solve a problem within 30 minutes, refer to the editorial. Learn any unfamiliar topics and repeat this process.
- As your rating improves, continue step 4 and solve problems within the rating range of [your rating - 100, your rating + 100].
- Keep learning new algorithms and practice implementing them.
-
How Problem Setters Find New Problems: Not all problems in contests are built from scratch. Many problems are a mixture of multiple problems from resources like the CSES Problem Set.
-
Getting TLE with String as a Key in Ordered Map: If you're experiencing performance issues with a string as a key in an ordered map, try using a hash map instead. This change may improve the performance.
-
IDE Recommendation: In competitive programming, it's recommended not to use an IDE. Instead, develop a habit of using a text editor like Vim.
-
Which Template Should I Use in CP?: There are various templates available for competitive programming. You can refer to the following resource for templates that are useful in competitive coding: Templates Useful for CP
-
Tips to solve Constuctive :
- Writing a brute force script rather than manual solving
- Finding a pattern
- coding optimized solution corresponding to pattern
- Taking care of edge cases.
Here's an implementation of the Ruffle Sort algorithm inspired by code from the second thread:
static void ruffleSort(int[] a) {
int n = a.length; // Shuffle, then sort
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int oi = random.nextInt(n);
int temp = a[oi];
a[oi] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
}
Arrays.sort(a);
}- start with array -> practice -> 2 🌟
- learn c++ stl or any language similar library, dp -> 3 🌟
- disjoint set union , graph, little dsa -> 4 🌟
- segment tree -> 5 🌟
- Codechef has very nice problems on Bit manipulation So , making good grip over bit manip can help in contest.
- Codeforces requires speed of solving problems.
- Even if you solve only 2-3 problems , but very quickly then , you will get fruitful ratings.
- Upsolving is required since the problem pattern might be repeated in future problems.
- First two questions are mostly greedy in div -2,3,4 contests. No prior knowledge except programming language is required.
- Below is example how upsolving looks like
If you encounter the error "Source should satisfy regex [^{}]public\s+(final)?\sclass\s+(\w+)" while using Java on Codeforces, follow this guide to resolve the issue: Troubleshooting Java Error on Codeforces
You can easily jump by 2 in Python using the range() function with a step size of 2. Here's an example:
for i in range(0, 10, 2):
print(i)Discover a lesser-known resource that can enhance your competitive programming skills: Heap using STL in C++
To avoid recursion depth problems in Python, you can increase the recursion limit using the following code:
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)Explore a collection of useful C++ tricks to enhance your programming efficiency: C++ Tricks on Codeforces
Feel free to explore these resources to overcome common challenges and improve your competitive programming skills.
Welcome to the repository! This README file provides important information and resources related to the project.
You can find the roadmap . It outlines the planned features, milestones, and overall direction of the project.
For additional information and insights, you can refer to the Codeforces blogs . These blogs cover various topics related to competitive programming and can be a valuable resource for learning and improving your skills.
Please keep in mind the following points:
- Number theory, bit manipulation, and dynamic programming (DP) are among the most popular topics in competitive programming.
- In 98% of the contests, at least one of these topics is always included.
- It is essential to practice these topics extensively to improve your proficiency.
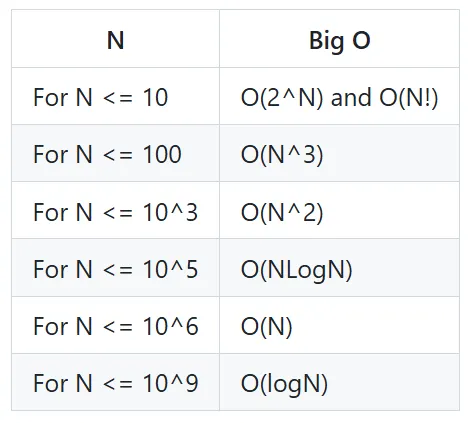
| N | Big O |
|---|---|
| For N <= 10 | O(2^N) and O(N!) |
| For N <= 100 | O(N^3) |
| For N <= 10^3 | O(N^2) |
| For N <= 10^5 | O(NLogN) |
| For N <= 10^6 | O(N) |
| For N <= 10^9 | O(logN) |
| channel |
|---|
| Tushar Roy |
| Striver |
| CodeNCode |
| Tech-Dose |
| Luv |
| Apna college Placement course |
| Errichto |
| William Lin |
| William Fiset |
| Algorithms live |
| benritmicocode |
| jonathan paulson |
| Second Thread |
| Topic Reference Link |
|---|
| Dynamic Programming Video |
| Mathematics for DSA & CP Video |
| Article Reference Link |
|---|
| Roadmap for Competitive Programming |
| Modulo Multiplicative Inverse |
| Random Shuffle |
- At maximum, a number can have O(2*sqrt(n)-1) factors, which is the upper bound for the number of factors.
- A leaf node is a node with a degree less than or equal to 1.
Please refer to the respective links for more information and resources related to coding, competitive programming, and problem-solving.
To configure Vim for competitive programming, follow the steps below:
- Open the terminal and enter the command:
vi ~/.vimrc - Paste the following configuration code into the file:
set number
set tabstop=4
set shiftwidth=4
set autoindent
set mouse=a
colorscheme default
autocmd vimEnter *.cpp map ^B :w <CR> :!clear ; g++ --std=c++17 %;if[[-f Output : ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++] a.out ];time ./a.out; rm a.out; if[[-f End : --------------------------------]a.out]<CR>
- Press
Ctrl+Cand thenCtrl+Bto compile and run the code.